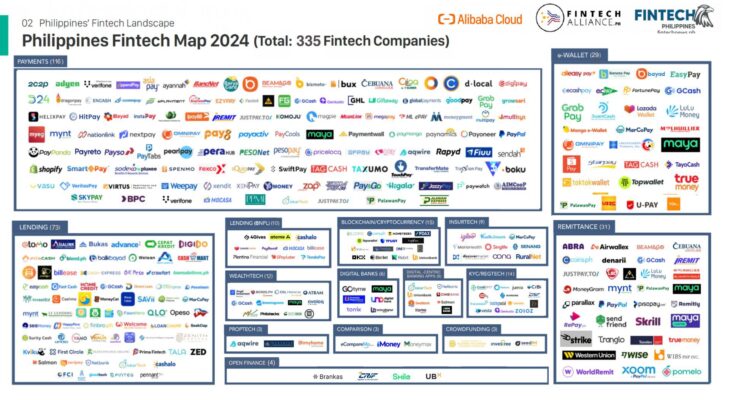
The Philippines Fintech Map 2024 provides a comprehensive overview of the rapidly expanding financial technology (fintech) ecosystem in the Philippines. As of 2024, this fintech landscape encompasses a total of 335 companies, spread across various sectors including payments, lending, e-wallets, blockchain, insurance, and more. The map gives us a clearer picture of how fintech is shaping financial services in the country, catering to the diverse needs of consumers and businesses alike.
1. Payments Sector (116 companies)
The payments sector is by far the largest in the Philippines’ fintech landscape, comprising 116 companies. These businesses offer various payment solutions ranging from digital wallets, payment gateways, point-of-sale (POS) systems, and money transfer services. Some of the leading players in this sector include:
- Gcash: One of the most popular mobile wallets in the Philippines, Gcash allows users to pay bills, transfer money, shop online, and even invest in financial products. Its user base has grown rapidly in recent years, driven by partnerships with merchants and financial institutions.
- Paymaya: Another leading digital payments provider, Paymaya offers both consumers and businesses the ability to send and receive payments. They also provide prepaid cards, making it easier for users without a bank account to participate in online transactions.
- PayPal: Although a global giant, PayPal is widely used in the Philippines, especially for international transactions, e-commerce, and freelance payments. It is a key player in facilitating cross-border payments.
- GrabPay: A service integrated into the Grab app, GrabPay allows users to pay for rides, food deliveries, and a range of other services within the Grab ecosystem.
- Alipay: Part of the larger Alibaba ecosystem, Alipay has begun making inroads in the Philippines, catering to both local and international consumers, particularly those involved in trade with China.
In addition to these heavyweights, the payments landscape also includes smaller players such as Dragonpay, Alyen, and Bizmo, which offer alternative payment methods and aim to capture niche markets.
2. Lending Sector (73 companies)
Lending is another key fintech sector in the Philippines, with 73 companies offering various forms of loans, including personal loans, payday loans, business loans, and micro-financing. The lending fintech companies have played a crucial role in addressing the financing gap in the country, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and underserved consumers who lack access to traditional banking services.
- TALA: A standout in the micro-lending space, Tala offers small, short-term loans to individuals through its mobile app. Using alternative data, the company assesses the creditworthiness of borrowers who may not have formal credit histories.
- Cashalo: This platform provides personal loans, allowing users to borrow money easily through their mobile phones. It is designed to provide accessible credit to Filipinos who need immediate financial assistance.
- BillEase: BillEase provides a buy-now-pay-later (BNPL) service that allows users to purchase goods and pay in installments. This offering has gained traction, particularly in e-commerce, as it gives consumers more flexibility with their payments.
Other noteworthy companies in the lending sector include Asialink, Home Credit, and Loan Solutions, each catering to different niches within the loan market.
3. e-Wallet Sector (29 companies)
The rise of digital wallets has transformed the way Filipinos handle money, and there are currently 29 companies operating in this space. E-wallets allow users to store funds electronically, make payments, and transfer money without needing a physical bank account. Some of the key players in the e-wallet sector are:
- GCash: As mentioned earlier, GCash is one of the most widely used digital wallets in the country. Its services include mobile payments, remittances, and even financial products like savings and investments.
- Maya: Formerly known as PayMaya, Maya is a versatile e-wallet that offers various financial services. Maya has also ventured into digital banking, giving users more reasons to engage with their platform.
- GrabPay: Initially integrated with Grab’s ride-hailing and delivery services, GrabPay is now a full-fledged e-wallet that allows users to make payments, transfer money, and more.
Additionally, other companies like Banana Pay, Lazada Wallet, and EasyPay are also contributing to the growth of e-wallet usage in the country.
4. Lending (BNPL – Buy Now, Pay Later) (10 companies)
The Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) segment has gained popularity in the Philippines, with 10 companies offering such services. BNPL allows consumers to purchase items and pay for them over time, usually without interest, which has proven appealing to a wide range of consumers, particularly those who may not have access to credit cards.
- Plentina: Plentina allows users to purchase goods from partner merchants and pay in installments. It is designed for the Filipino market, where traditional credit is often out of reach for many consumers.
- TendoPay: TendoPay is another BNPL platform that provides users with the flexibility to make purchases and pay in easy installments. It is increasingly being used in e-commerce and retail.
Other notable BNPL players include Atome, BillEase, and 4Gives, all of which offer consumers more flexible payment options.
5. Blockchain/Cryptocurrency (15 companies)
Blockchain and cryptocurrency are relatively new but growing sectors in the Philippine fintech landscape, with 15 companies operating in this space. These companies are focused on providing crypto trading platforms, blockchain solutions, and other related services.
- Coins.ph: One of the most well-known cryptocurrency platforms in the Philippines, Coins.ph allows users to buy, sell, and store cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. It also provides mobile wallet services.
- PDAX: The Philippine Digital Asset Exchange (PDAX) is a regulated cryptocurrency exchange that enables users to trade cryptocurrencies in a secure and compliant manner.
- Binance: A global cryptocurrency exchange, Binance has a significant presence in the Philippines, allowing users to trade a wide variety of digital assets.
In addition to these platforms, companies like Rebit and UnionBank are also exploring blockchain solutions for remittances and financial services.
6. Insurtech (9 companies)
The Insurtech sector consists of 9 companies, which focus on improving the insurance industry through technology. These companies are making insurance more accessible to Filipinos by offering digital solutions for purchasing, managing, and claiming insurance policies.
- Kwik.insure: A digital insurance platform, Kwik.insure makes it easier for consumers to compare and purchase insurance policies online.
- Oona: Oona is a new digital insurance platform that offers health and travel insurance, among other products. It leverages technology to simplify the claims process and improve customer experience.
Other notable companies in the insurtech space include Singlife and Maria Health, both of which focus on streamlining the insurance process for consumers.
7. Remittance (31 companies)
Remittances are a crucial part of the Philippine economy, and there are 31 companies operating in this space. These fintech firms offer services that make it easier and more affordable for overseas Filipino workers (OFWs) to send money back home.
- Western Union: One of the oldest and most well-known remittance services, Western Union has a strong presence in the Philippines, offering both physical and digital remittance services.
- WorldRemit: WorldRemit allows users to send money online to the Philippines, with options for bank transfers, mobile money, and cash pickups.
Other prominent companies include MoneyGram, Coins.ph, and GCash, each contributing to the growing remittance market.
8. WealthTech (12 companies)
WealthTech, which includes platforms focused on investment and wealth management, consists of 12 companies. These platforms are democratizing access to investment opportunities for Filipinos, allowing even those with small amounts of capital to invest in various financial products.
- Seedbox: Seedbox offers an easy-to-use platform where users can invest in mutual funds and other financial instruments. It provides educational resources to help new investors get started.
- ATRAM: ATRAM is another investment platform that offers a range of financial products, including mutual funds and asset management services.
9. Other Categories
- PropTech (4 companies): Platforms like Aqwire and MyHome focus on property technology, helping users buy, sell, and manage real estate digitally.
- Open Finance (4 companies): Companies like Brankas focus on enabling open finance, making financial services more accessible through APIs and data sharing.
- Digital Banks (6 companies): Companies like Maya Bank and Tonik are leading the charge in digital banking, offering online-only financial services.
- Crowdfunding (3 companies): Investree and SeedIn are key players in the crowdfunding space, helping small businesses raise capital from individual investors.
Conclusion
The Philippines’ fintech landscape in 2024 is diverse and dynamic, with a wide range of companies offering innovative financial solutions across payments, lending, e-wallets, blockchain, insurtech, and more. This ecosystem is poised for further growth as fintech continues to play a critical role in expanding financial inclusion and providing modern financial services to Filipinos.